From meeting medically complex patient needs to improving financial performance, post-acute care integration has never been more important for a hospital’s overall strategy.
Read this guide to learn the top trends in rehabilitation for 2023 and hear from Lifepoint Rehabilitation President Russ Bailey on how these trends are expected to impact hospitals.
1. Combating the Ongoing Workforce Crisis
Recruiting and retaining high-performing clinical talent remains a top priority, according to a recent McKinsey and Company healthcare executive survey. While this may be no surprise, three key factors fueling this ongoing shortage include:
Elevated Staffing Costs
Due to various COVID-19 surges, labor costs have grown 25% since 2019.1 “It has become increasingly difficult for hospitals to keep up with service demands with a drastically declining workforce,” shared Bailey. “This has forced hospitals to compete for talent, therefore pushing the financial envelope across the continuum.”

The talent shortage is not only increasing labor costs, but overall healthcare costs. By 2025, it is projected there will be a gap of nearly 450,000 nurses and 80,000 doctors.2 If this trend continues, the labor shortage will outpace inflation.
Support from a focused post-acute partner with local and national reach helps hospitals to identify and retain specialized talent. This is made possible through national data and resources that can help a hospital locate qualified candidates across the nation. When the right team members are in place, patient satisfaction, outcomes and employee retention all increase.
Worsening Experience-Complexity Gap

In addition to the overall labor shortage, hospitals are facing a new kind of shortage among the clinical workforce: experience.3 New nurses are not entering the field at the same rate as retirement-age nurses are exiting the workforce.
“Not only are we seeing a large gap in experienced clinical labor, the patient population is becoming older and more complex. With rising comorbidities, more standardized protocols and shorter lengths of stay, hospitals are actively seeking support from an industry expert to help alleviate this labor-patient imbalance,” stated Bailey. A specialized partner can provide more experienced team members to help hospitals provide high-quality clinical care.
Capacity Constraints
A lack of clinical labor, treatment supplies and bed space has heightened the healthcare labor crisis. Bailey said, “We have come to understand that these compounding factors cannot be taken on by a single hospital. External support from a focused partner allows hospitals to focus on quality care while the partner provides specialized resources and expertise to overcome challenges such as capacity constraints.”
2. Scaling Chronic Disease Management
As more patients experience multiple chronic conditions, hospitals are seeking resources to effectively meet the need within their local community.
For example, more than 655,000 people in the U.S. die from heart disease each year, while nearly 800,000 experience a stroke annually.4 At the continued rate of increase, the direct and indirect costs for these two illnesses could reach $1.1 trillion by 2035.5 “Seeing cases like heart disease and stroke drastically rise each year, and the costs associated with each, is just one of the many reasons hospitals are including elevated chronic disease management into their overall strategy,” stated Bailey.
“Hospitals can’t operate at the same level they did 20 or even ten years ago – patient needs are far too complex now. When Lifepoint partners with hospitals, we bring in the latest specialized technology, training and expertise to help equip staff with resources to succeed with their patients, no matter their condition.” Having a post-acute partner who can help enhance access to specialized quality care within a hospital’s local community is important to address chronic and complex illnesses, and improve the community’s overall health.
3. Leveraging Flexible Care Models
COVID-19 highlighted the need for bed flexibility and evolving care models. In response, hospitals are reviewing the scope and scale of their care continuum. This is leading to service line expansions, and an increase in ambulatory sites, digital health, primary care and post-acute care.6
![]()
Co-location, or the integration of multiple care settings on one hospital campus, continues to see substantial growth as patients with both physical and mental illnesses want to receive high-quality care in the same setting. This model, also referred to as the Hospital-in-Hospital (HiH) model, helps streamline a hospital’s care approach and serves as an effective strategy for overall outcomes and flexibility.
“When you pair post-acute services with one another under the same roof, you enable patients to reap the benefits of multiple specialty offerings without having to transfer them outside of the system,” stated Bailey. “For example, when you have inpatient rehabilitation and behavioral health in the same hospital, physicians can spread their skill set across service lines. This not only increases flexibility for staff, but can ultimately reduce patient readmission risk and care cost.”
Implementing the co-location or HiH model into a hospital’s care continuum opens the door for additional growth, and further strengthens reputation, service optimization and financial stability.
4. Focus on Financial Stability
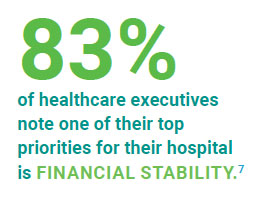
Eighty three percent of healthcare executives note one of their top priorities for their hospital is financial stability when looking at their strategic plans for 2023, according to a recent Healthcare Financial Management Association (HFMA) survey.7
“Successfully managing all aspects of a rehabilitation unit or hospital has become more financially challenging due to growing patient complexities, readmission risks and the expansion of valuebased care integration,” stated Bailey. “If a hospital can achieve an effective post-acute strategy they can better manage the intricacies of the program and increase care quality in a cost-conscious way.”
![]()
As managed care and other value-based reimbursements become a larger part of the equation, it will be even more important to conduct care in a way that makes the most of the limited funds available to hospitals. A post-acute partnership can aid in a successful transition to value-based care and help equip hospitals with the resources to increase care quality and efficiency. This can help reduce readmission risk and generate long-term cost savings for the entire hospital.
5. Growth of Strategic Partnerships
The rise in complex illnesses, growth in consumer expectations and an increasing emphasis on affordable and high-quality care have shifted the healthcare landscape. Throughout the pandemic, health leaders turned to innovative solutions to effectively meet the growing demand in their community. Contract management and joint-venture partnerships emerged as a proven strategy to expand care in a high-quality and cost-effective manner.
![]()
“Strategic partnership offers access to new capabilities, increased speed to market, and greater efficiencies in capital, scale and operations,” stated Bailey. “For instance, partnership with Lifepoint Rehabilitation allows local hospitals to access a national database of quality data, greater operational efficiency and industry-leading best practices. We offer a robust team of clinicians and rehabilitation professionals all focused on making their program successful. Through our partnership solutions, we are able to relieve the burden of running a complex service line, enabling hospitals leadership to focus on what really matters – the patient.”
How We Can Help
Through a history of successful joint-venture partnerships and contract management agreements, Lifepoint Rehabilitation works with leading health systems across the country to more effectively meet the needs of their patients, drive employee satisfaction and generate long-term quality outcomes for their organization.
References
- Fleron, A., Krishna, A., & Singhal, S. (2022, September 19). The gathering storm: The transformative impact of inflation on the healthcare sector. McKinsey & Company. Retrieved September 21, 2022, from https://www.mckinsey.com/ industries/healthcare-systems-and-services/our-insights/ the-gathering-storm-the-transformative-impact-of-inflationon- the-healthcare-sector
- Berlin, G., Lapointe, M., Murphy, M., & Wexler, J. (2022, August 1). Assessing the lingering impact of covid-19 on the nursing workforce. McKinsey & Company. Retrieved September 21, 2022, from https://www.mckinsey.com/ industries/healthcare-systems-and-services/our-insights/ assessing-the-lingering-impact-of-covid-19-on-the-nursingworkforce
- The Advisory Board (29, June 25). The experience-complexity gap. Advisory Board. Retrieved September 21, 2022, from https://www.advisory.com/topics/nursing-care-quality-andservice/ 2019/06/the-experience-complexity-gap
- Souders, A. (2022). Heart Disease and Stroke Prevention FY 2023 Fact Sheet. National Association of Chronic Disease Directors. https://chronicdisease.org/wp-content/ uploads/2022/04/NACDD-Fact-Sheet-2023_DHDSP-final2.pdf
- American Heart Association. (2017). Cardiovascular Disease: A Costly Burden for America https://www.heart.org/-/media/ Files/About-Us/Policy-Research/Fact-Sheets/Public-Health- Advocacy-and-Research/CVD-A-Costly-Burden-for-America- Projections-Through-2035.pdf
- Singhal, S., & Patel, N. (2022, August 5). The future of US healthcare: What’s next for the Industry Post-covid-19. McKinsey & Company. Retrieved September 22, 2022, from https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/healthcare-systemsand- services/our-insights/the-future-of-us-healthcare-whatsnext- for-the-industry-post-covid-19
- HFMA, (June 2022), Rehabilitation Service Live Survey, [PowerPoint Slides], Healthcare Financial Management Association

